Ihr Warenkorb ist gerade leer!
White Paper: Strategic Success Potentials in Times of Disruption
Part 1 of 2
Just as operational management has its controlling or core figures in annual or quarterly earnings figures, so too does its strategic management. The most important control variables here are the market position, the cost position and the customer benefit. Add to this the handling of new technologies and here come S-curves and disruption into the game. The interplay of these variables allows us to derive the success potential and thus the future viability of a company.
Download this page as PDF
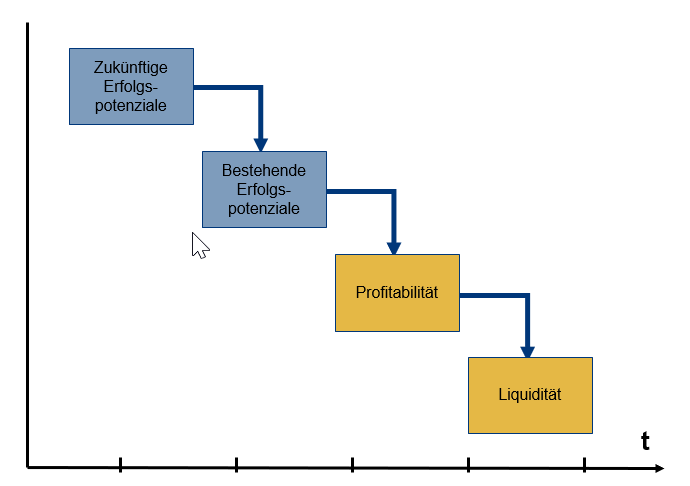
Strategic success potentials
Success potentials are all the prerequisites and abilities of a company, with which the results of the enterprise are achieved. Gälweiler differentiates here by distinguishing between current and future potential for success.
Today’s potential for success
Today’s or existing potential for success forms the basis for the medium-term success of the company. The most important key figures for this are the market position and the cost position. However, these key figures are not sufficiently informative about the long-term success and survival of the company.
Future success potential
Future success potential ensures that a company can remain successful in the long term. The central control parameters for this are the «solution-independent customer problem» and «new technologies». The building up of future success potentials is attributed to the strategic management. Essentially, the development of future success potentials corresponds to innovation and thus to strategic innovation management.
«Strategic corporate governance as a precontrol task with regard to the subsequent realization of success therefore consists of the search, creation and maintenance of high and secure success potentials, which always includes the timely location of innovation potential.»
(A. Gälweiler, 1987)
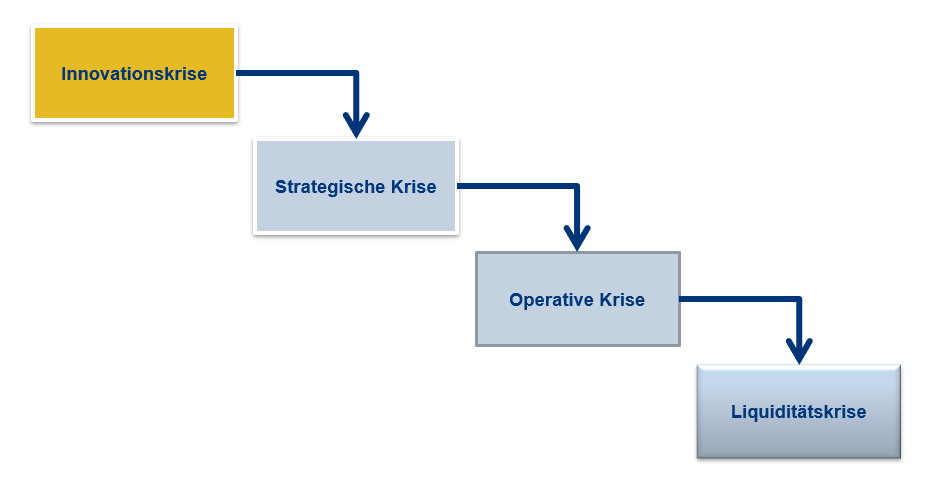
The different crises of a company
According to this logic, corporate crises can be classified:
- If a company lacks the liguidity, it is technically bankrupt and one calls this the «liquidity crisis». This happens to many startups – although you have good business models and a lot of potential when you run out of money, that’s over
- The operating crisis or earnings crisis occurs when the profit is down or negative. This is not the death of a company. As long as money is there, it can survive and if the strategy is right, it will even be back in the black.
- The strategic crisis is defined by a poor market and cost position. The gain may still be positive, but the future is endangered.
- The innovation crisis will only take effect in a few years, when new solutions based on new technologies begin to substitute our products and services.
Gälweiler on operational key performance indicators versus strategic success factors
Quotes from A. Gaelweiler: Strategic Management, 1987
- The autonomy of strategic corporate management lies above all in its independent orientation. (P. 26)
- The autonomy of strategic corporate management lies above all in its independent orientation (p. 26) Operational business data, as important and irreplaceable as they are for running the day-to-day business, often leaves the actual strategic problems of a business venture in one Light that does not correspond to the real strategic conditions. Therefore results and data of the current business usually lead to a strategically wrong behavior. (P. 25)
- Success data are relatively ineffective and often totally misleading as a basis for strategic corporate governance. (P. 30)
- The signals emanating from the short-lived success data are usually not only too late. Too often, they also mislead to acting in a long-term, wrong-pointing direction without first being noticed. (Pp. 240 f.)
- Last but not least, therefore, the fundamental importance of the strategic management task lies in the fact that wrong decisions and omissions are generally no longer correctable or recoverable if they only become noticeable at the time of the operational implementation of the success data. (P. 26)
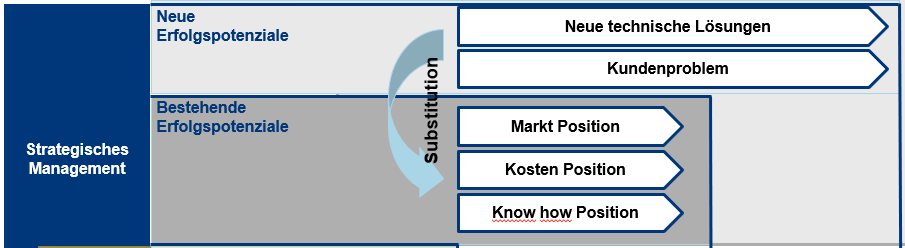
The current success potentials and their control parameters
According to Gälweiler, today’s potential for success is derived from the control factors of the cost position and the market position. From our point of view, it is indispensable to include the area of employees as a further position for control variables. Our experience shows that this as a strategic success potential also plays a crucial role.
Market position
The control parameters of the market position include the following factors:
- Absolute market share
- Relative market share (in relation to the 3 biggest competitors)
- Customer loyalty
- Customer Value
- Relative Qualitä
- Image
- entry barriers
These figures show whether your own market position can be maintained and defended, or expanded.
Cost position
The control variables of the cost item are the various types of productivity. The continuous optimization of structures and processes comes into play here:
- Productivity of knowledge
- Productivity of the invested capital
- Productivity of employees
Know-how Position
The active involvement of employees in corporate development releases strong and often unimaginable energies and decisively supports the development of factors such as:
- Know-how
- Core competences
- Motivation and commitment
- Creativity and new ideas
Future success potentials and their control variables
Gälweiler derives the future potential for success from the control parameters of customer benefits and technologies.
Customer benefits
Customer value is the anchor for any corporate strategy; And this is about the original customer problem, detached from the product or offer. We also refer to this as a «solution-independent customer problem». Whether you prefer to call the customer problem a customer request or a customer need, leave it to them. We treat these three terms as synonyms.
Here are the questions:
- What does the customer really pay for?
- For what does he put the money on our counter and not go to the competition?
A detailed description of this topic can be found in our whitepaper «Customer Benefits».
Technologies
All technologies have a limited lifetime because they are replaced by new and improved technologies. There are on the one hand gradual improvements and optimizations of existing technologies, on the other hand quantum leaps, with which a new technology replaces the existing solutions within a short time. Not only does it offer improved solutions, it also offers completely new applications that are better for the customer. These are e.g. the automobile with the internal combustion engine opposite the horse-drawn carriages or the email via the Internet opposite the letter post. As control parameters of the technologies the questions after the
- right key technologies
- the life phase of an existing key technology
- the advent of new technologies
- your own core competencies
- the substitution of existing products and solutions
Disruption and S-curve
Here we find the basis of what is being discussed and treated nationwide under the term «disruption»: the S-curve.
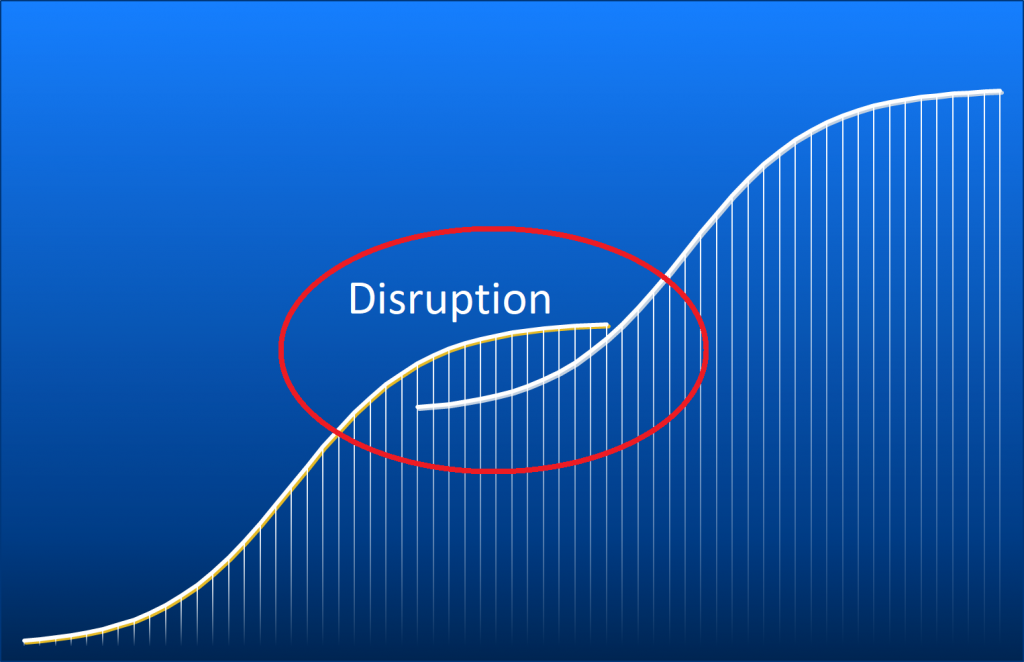
The expiration of a technology while at the same time a new technology spreads, shows the emergence of future success potentials. Existing products are substituted by new offers according to the pattern of the S-curves.
In the next whitepaper, we will discuss it in detail and introduce the S-curve tool in more detail.
Download this page as PDF
Ignaz Furger
Furger and Partner Inc Strategy Development Hottingerstrasse 21 CH – 8032 Zurich +41 44 251 8070 furger@furger-partner.ch www.strategy.app
Schlagwörter:
Schreiben Sie einen Kommentar